

It has been associated with tasks that require repetitive and intensive hand activities, particularly when these are carried out in constrained postures. Radial nerve injuries have distinct signs and symptoms depending on where and how the nerve has been injured.Ĭhanged vibration threshold and loss of nerve movement in patients with repetitive strain injury the peripheral neuropathology of RSI Repetitive strain injury (RSI) is a chronic pain condition affecting the upper limbs. Sensory function: Two-point discrimination on the dorsum of the thumbĪ thorough physical exam is always required. Motor function: Thumb extension against resistance The following tests can quickly assess the radial nerve and its motor and sensory functions: Posterior cutaneous nerve (arm and forearm) The radial nerve divides into a deep (mostly motor) branch, which becomes the posterior interosseous nerve (PIN), and a superficial branch.
#Radia nerve skin#
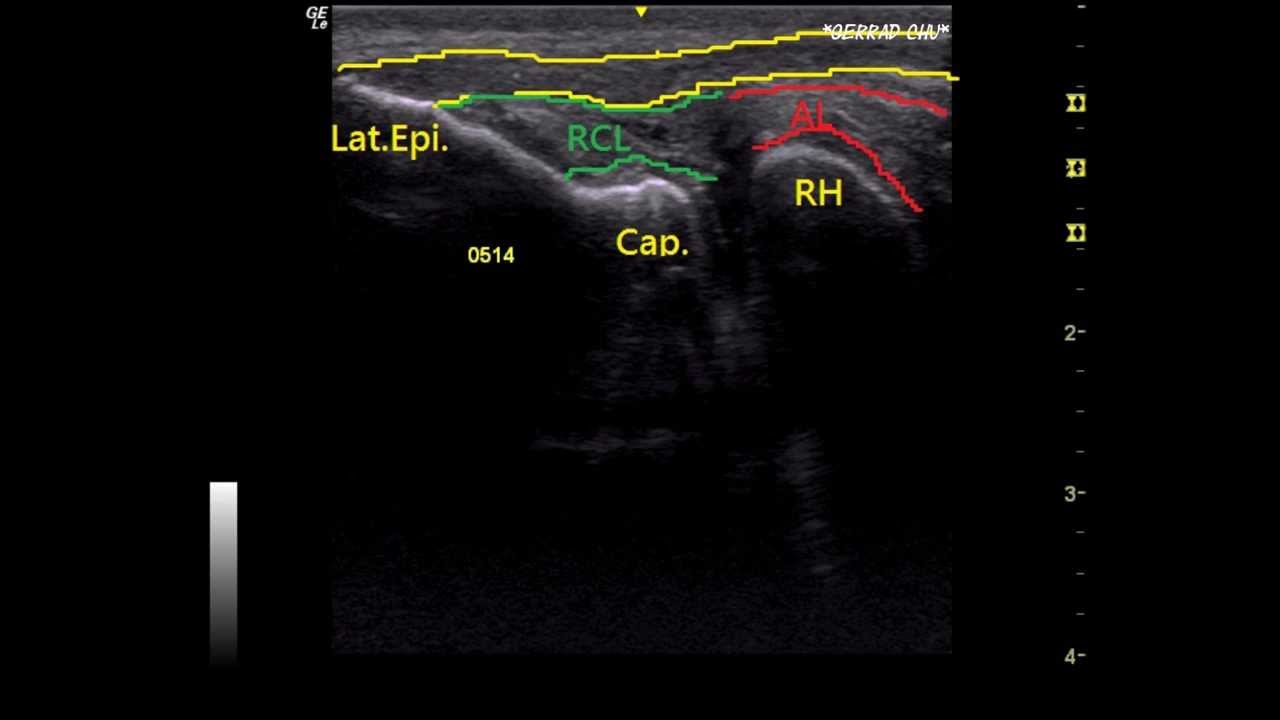
It also supplies the triceps brachii muscle of the arm, the muscles in the posterior compartment of the forearm (also known as the extensors), the wrist joint capsule, and aspects of the dorsal skin of the forearm and hand. The return of function following radial nerve palsy follows a predictable clinical pattern. Brachioradialis followed by ECRL are the first to return whereas, EPL and EIP are the last to return.The radial nerve stems from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus and supplies the upper limb. If available, this modality can be used for evaluation. There was a recent study of rapid ultrasonographic diagnosis of radial entrapment neuropathy at the spiral groove. It is important to note that more than 90% of radial nerve palsies will resolve in 3 to 4 months with observation alone.
#Radia nerve serial#
EMG/NCS is also utilized for follow-up management in serial observations for the return of nerve function. Occasionally, when ruling out or investigating compressive neuropathies, advanced imaging such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can further delineate pathological anatomic determinants.Įlectromyograms or nerve conduction studies (EMG/NCS) can help differentiate nerve versus muscle injury, measuring the speed at which the impulses travel along the nerve. When there is a traumatic injury, radiographs are usually adequate. This is especially relevant after traumatic injuries such as fractures. Injuring the radial nerve distal to the elbow joint can occur from:
Any condition or clinical situation in which the patient has improperly created pathologic forces and/or compression in the axilla can potentially affect the radial nerve by way of the brachial plexus.
There will also be a sensory loss in the posterior aspect of the forearm, radiating to the radial aspect of the dorsal hand and digits. This is seen commonly with "Saturday night palsy" and improperly using crutches (crutch palsy). There will be a sensory loss in the lateral arm. Thus, this usually presents with a wrist drop on physical examination. If damaged at the axilla, there will be a loss of extension of the forearm, hand, and fingers. However, when the hand is pronated, the wrist and hand will drop. This is also referred to as "wrist drop.” With the hand supinated, and the extensors aided by gravity, hand function may appear normal. He or she may complain of decreased or absent sensation on the dorsoradial side of their hand and wrist with an inability to extend their wrist, thumb, and fingers. A patient with radial neuropathy may present holding their affected extremity with the ipsilateral (normal) hand.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
